HFMI – fatigue
What are fatigue cracks?
In many applications fatigue is one of the main reasons of degradation of welded structures, together with corrosion and wear.
Cyclic loads and vibrations occur in most mechanical applications:
- machinery (harvesters, hoists, cranes, etc.)
- transport (ships, trailers, trains, etc.)
- steel construction (bridges, sluices, etc.)
One can distinguish 4 situations:
- The occurrence of fatigue cracks is normal if the component meets the foreseen lifetime.
- Fatigue cracks are a problem when they appear early. Early fatigue cracks can be caused poor weld quality,
- Overload (effective load is higher compared to design stress)
- Too weak design.
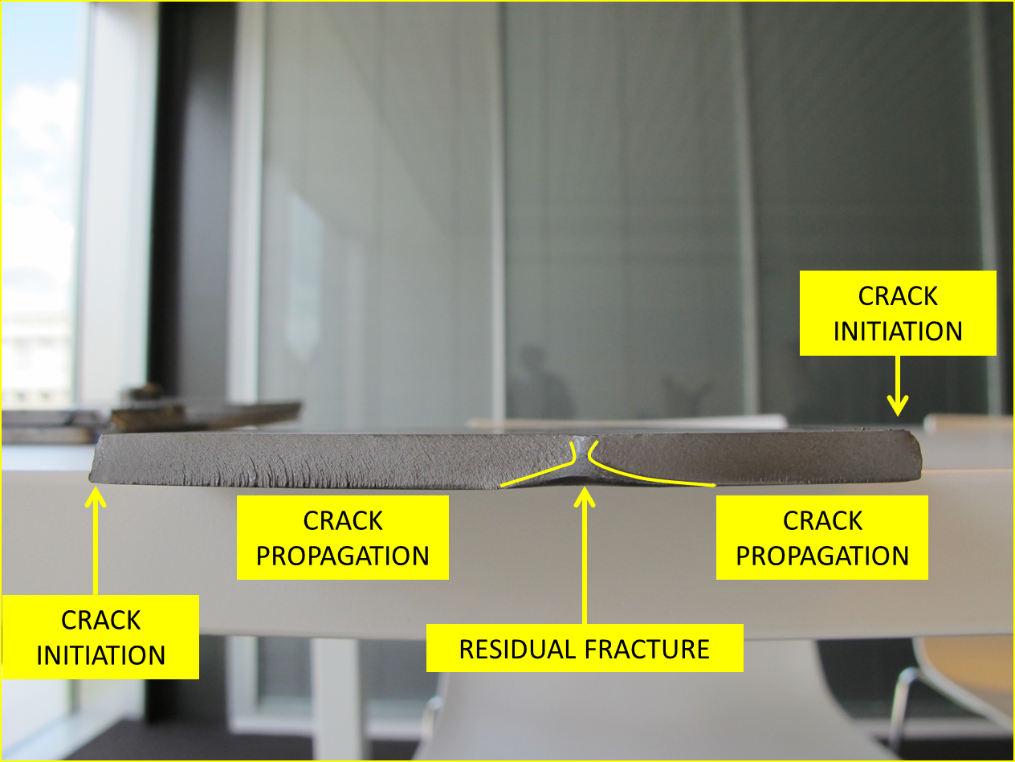
Cyclic loading cause fatigue cracks, and most often these cracks occur near welded joints. A fatigue crack happens in 3 stages:
- crack initiation at a stress raiser point
- crack propagation (slow process). The crack surface can be recognized by its ‘beach marks’
- the residual fracture. This occurs when the remaining sections it too small to bear the load
What it the most effective way to prevent fatigue cracks?
In most cases, except for poor weld quality, there is a simple solution to increase fatigue life of welded joints: it is the HFMI treatment of the most critical welds (High Frequency Mechanical Impact treatment). This technology relies on the introduction of beneficial compressive stress around welds.
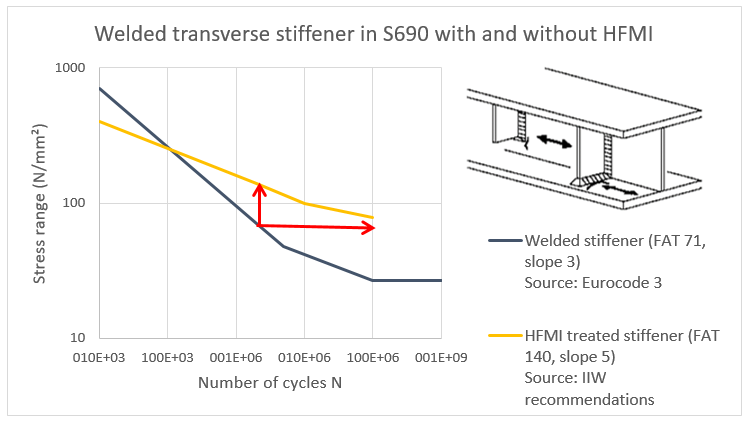
The S/N curves below shown the fatigue properties of transverse stiffeners in S690 in as welded condition and post weld treated with HFMI. These curves are marked by the FAT class (allowed design stress for a life expectation of 2M cycles) and a slope.
The post weld treatment increases the FAT class from 71 up to 140 N/mm² (vertical red arrow). Or at equal stress, the life expectation increases from 2M cycles up to 100M cycles (horizontal red arrow). It shows that HFMI can extend the fatigue life of welds drastically. Furthermore, it is a solution for components which are designed too weak and show early fatigue cracks.
In an article published in Welding and Cutting in 2015, practical examples of HFMI are described (PIT applied in a potato harvester, an industrial washing machine and hoists.) Downloadlink article
Baaten Welding Consultancy offers:
- Help with designing welded structures which are subjected to fatigue. By finite elements calculations the hot spots can be indicated. Based on these calculations, an approach for HFMI can be decided.
- Application of HFMI.
- HFMI training.
S/N curve of a transverse stiffener in as welded condition and post weld treated with HFMI (Source: Eurocode 3: Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures and de IIW Recommendations for the HFMI Treatment For Improving the Fatigue Strength of Welded Joints - G. Marquis, Z. Barsoum)